Optimization in CSP plants in Chile; second Doctoral Thesis in our Chair
November 14, 2025
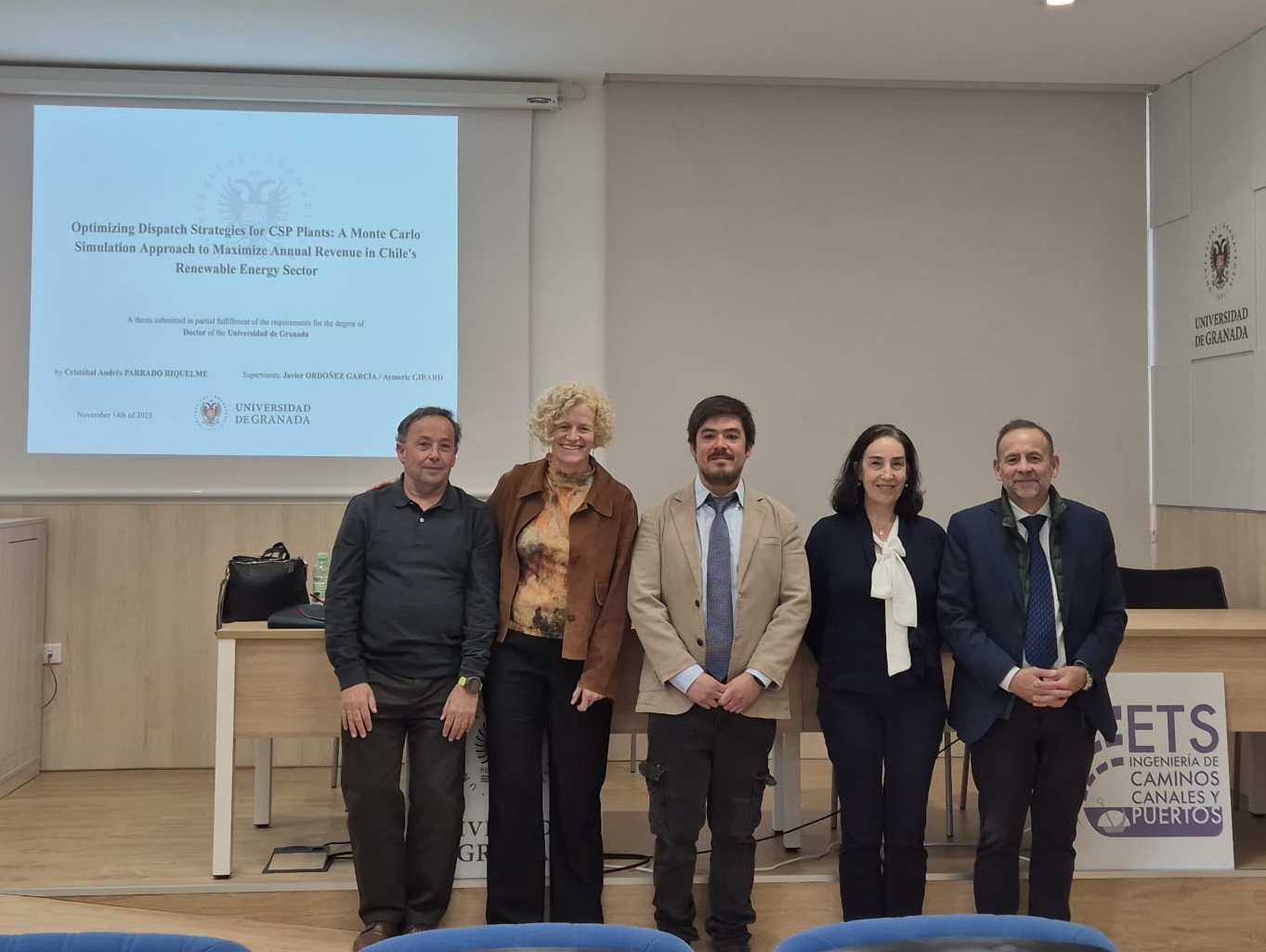
After several years of collaboration, and overcoming numerous challenges, on November 14, our collaborator and professor at Andrés Bello University, Cristóbal Parrado, successfully defended his doctoral thesis entitled "Optimizing dispatch strategies for CSP plants: a monte Carlo simulation approach to maximize annual revenue in Chile's renewable energy sector" before a committee composed of Professors
M. Begoña Moreno (UGR) y Rosalía Pacheco (UPM), and
Juan Carlos Rubio (UMA).
Supervised by Prof. Javier Ordóñez (director of our Chair) and Prof. Aymeric Girard, and presented under the slogan "Taming the Sun", his defense was thorough, clear, and informative, earning the highest possible grade from the committee.
Congratulations Cristóbal!
Thesis at the University of Granada

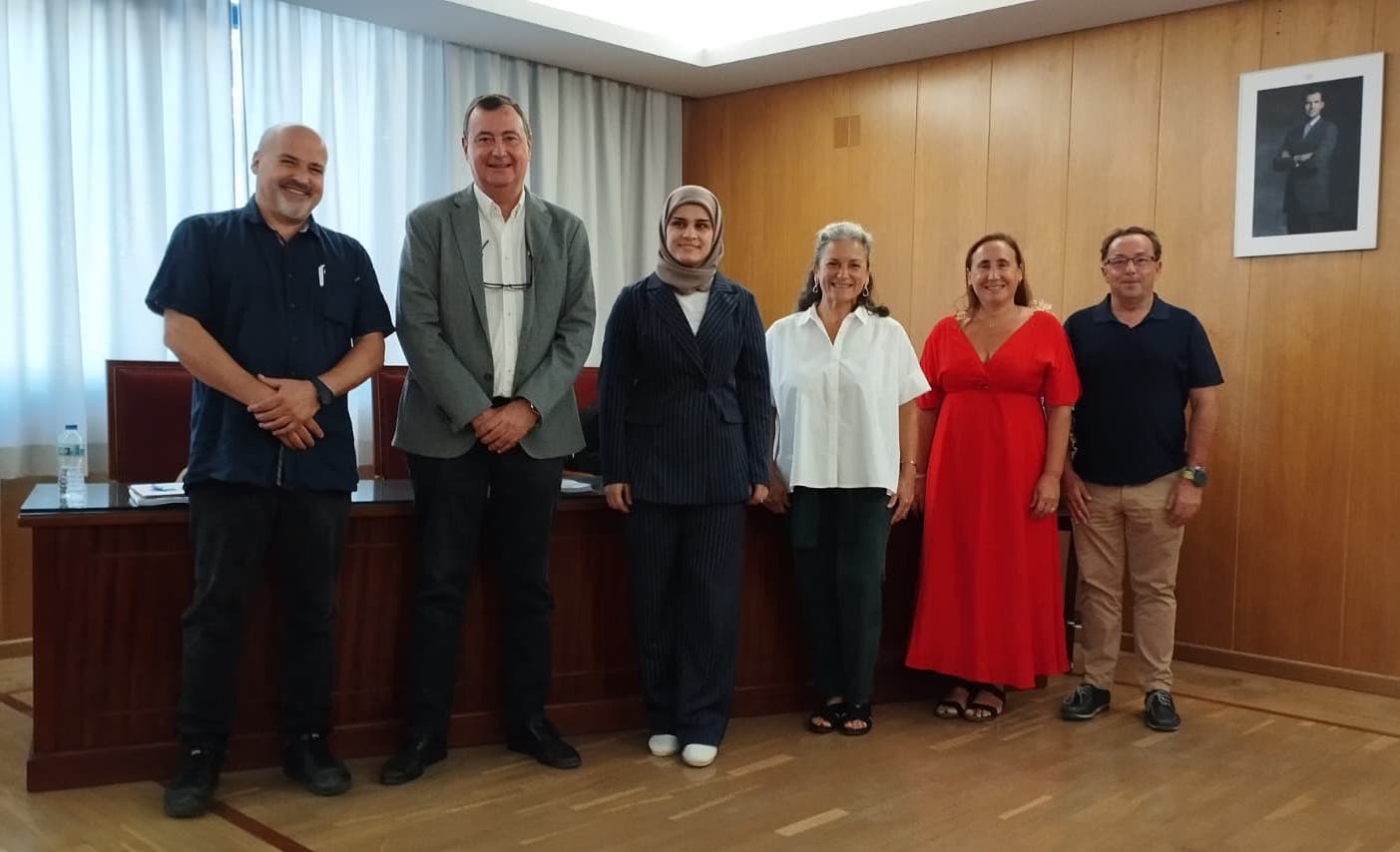
Optimization of Renewable Energy Microgrids in Iraq; Doctoral Thesis within the UNESCO Chair
September 11, 2025
We began the academic year with the PhD disertation of our youngest member, Kawakib Tahir, who defended it before the panel composed of Professors Ángela Barrios-Padura (USE), Mónica López Alonso (UGR), and Eugenio Pellicer Armiñana (UPV). This committee decided to award the highest grade to this thesis, entitled "Strategic Optimization of Hybrid Microgrid Systems for the Transition to Renewable Energy: A Comprehensive Study with Application Cases in Iraq" supported by 5 publications and supervised by Professors Javier Ordóñez and Juanjo Nieto, both members of our Chair.
Congratulations, Kawakib!
All doctoral theses from the UGR

Intense drought and vegetation browning exacerbate air temperature rise in unirrigated peri-urban areas under global warming
Julio de 2025
This study analyzes 63 years of data from Santiago, Chile, and reveals an alarming fact: peri-urban areas, with permeable soils and little vegetation, are warming faster than urban centers and parks. Lack of irrigation and droughts intensify this effect, generating significant temperature differences and greater social and environmental vulnerability. The research shows that urban design and water management are key to slowing accelerated warming in these areas, where moisture loss turns the soil into a heat amplifier.
This finding relates to SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and SDG 13 (Climate Action), highlighting the importance of adapting cities to extreme weather events. It also connects with SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), stating that water resource management is essential to mitigating urban heat, and with SDG 15 (Life on Land), highlighting the importance of conserving vegetation in metropolitan environments. See the full article in: Sustainable Cities and Society
Read the full article in open access at: Sustainable Cities and Society

Modeling Intra-Organization Fragmentation and Integration to Enhance Performance in Industrialized Timber Construction
Junio de 2025
Industrialized construction, especially wood construction, promises efficiency and sustainability, but faces a serious problem: fragmentation among design, production, and assembly teams. This study, using the Virtual Design Team methodology, models and simulates how a lack of integration generates delays, rework, and higher costs in a Chilean modular construction company. The results are clear: when early collaboration is encouraged, errors are reduced, timelines are shortened, and final quality improves. Integrating teams is not only a matter of organization, but also a strategy to increase competitiveness in the sector.
This advancement directly contributes to SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) by promoting more efficient, resilient, and less wasteful construction systems. It also improves productivity with a lower environmental impact, also aligning with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), promoting optimized and sustainable industrial processes.
Read the full article in open access at: Buildings

Optimization Techniques and Software for Hybrid Microgrid Systems
April 2025
This study reviews optimization techniques and software for improving the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and energy reliability of hybrid microgrid systems. After analyzing 4134 documents in Scopus, we classified the techniques into classical methods (16.87%), metaheuristics (47.12%), and AI-based methods (36.01%), highlighting the predominance of metaheuristics and the growing role of AI-driven approaches in real-time decision-making. Additionally, 2667 documents on software were analyzed, identifying MATLAB/Simulink (65.34%) and HOMER (22.08%) as the most frequently used tools for simulation, modeling, and technoeconomic analysis.
This study identifies key research trends, highlights shortcomings in optimization strategies, and emphasizes the need to integrate AI, expand the adoption of open-source tools and scalable optimization frameworks, providing valuable insights not only for researchers but also for policymakers and industry professionals, supporting the development of sustainable and cost-effective HGM solutions.
See the full open-access article at: Energies

Using Timber in Mid-Rise and Tall Buildings to Construct Our Cities: A Science Mapping Study
February, 2025
Timber construction is no longer limited to small houses: thanks to products such as cross-laminated timber (CLT), it is now possible to build mid- and high-rise buildings that compete with concrete. This study analyzes the scientific evolution of the topic, revealing that research has moved from basic aspects to advanced structural solutions, seismic performance, and social perception studies. Furthermore, sustainability remains a central focus, with an emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and life-cycle analysis. The use of high-rise timber not only responds to an architectural trend, but also to an urgent need to decarbonize our cities.
This approach is directly linked to SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), SDG 13 (Climate Action), and SDG 15 (Life on Land), as it promotes the use of renewable resources from sustainably managed forests and reduces emissions in construction. In addition, it promotes technological innovation and urban resilience, contributing to SDG 9 through the development of cleaner and more efficient infrastructure. Read the full article in open access at: Sustainability

Sustainable mobility: how to make our cities cleaner and more efficient
February, 2025
More and more European cities are limiting car use in their city centres to reduce pollution and improve quality of life. How can citizens move around without problems if they cannot use their car in the centre? This is where Park and Ride (Park & Ride) parking comes into play.
This study applies a modified multi-criteria decision method, using the Mahalanobis distance, to classify P&R according to environmental, economic, functional and social criteria. The results allow authorities to identify the most sustainable solutions and prioritise improvements in urban mobility. Thanks to scientific tools like this, administrations can make more informed decisions to improve public transport, reduce traffic jams and decrease pollution. Sustainable mobility is not only a challenge, but a great opportunity to transform our cities into more accessible, efficient and healthy places for everyone.
This type of research is essential to move towards cleaner and more liveable cities, an objective also pursued by our UNESCO Chair on Sustainable Development and Environment. In fact, initiatives like this are aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals, in particular SDG11 (Sustainable cities and communities) and SDG13 (Climate action).
Read the full article in open access at: Journal of Civil Engineering and Management

Urban heat islands' effects on the thermo-energy performance of buildings according to their socio-economic factors
December, 2024
Cities not only concentrate people, but also heat. This phenomenon, known as Urban Heat Island (UHI), raises temperatures in dense areas, affecting thermal comfort and energy consumption. This study shows that neighborhoods with lower socioeconomic status are more vulnerable because they have less vegetation and less insulated homes. UHI increases the need for cooling in summer and poses risks of overheating, which exacerbates inequality and energy poverty. Designing cities resilient to extreme heat becomes essential.
This problem connects with SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) because it demands equitable and adaptive urban planning. Furthermore, it is related to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) by highlighting the need for passive solutions and energy efficiency. Adapting to these challenges is also part of SDG 13 (Climate Action), since mitigating the effects of urban warming involves measures to address climate change.
Read the full article in open access at: Developments in the Built Environment

From diesel reliance to sustainable power in
Iraq: Optimized hybrid microgrid solutions
November 19th, 2024
This study analyzes Iraq's electricity crisis situation, worsened by wars and frequent power outages. It critiques reliance on diesel generators and advocates transitioning to solar photovoltaic (SPV) systems, strongly supported by experts. Using adapted load data using the innovative ROSETTA transform, SPV was found technically viable but currently more expensive than existing rates. A hybrid microgrid system combining SPV and batteries emerged as the most economical solution, with quick cost recovery. The research highlights the need for a shift toward sustainable energy for Iraq's future.
See whole open source article on Renewable Energy

Automated precise seeding with drones and AI: A workflow
July 2024
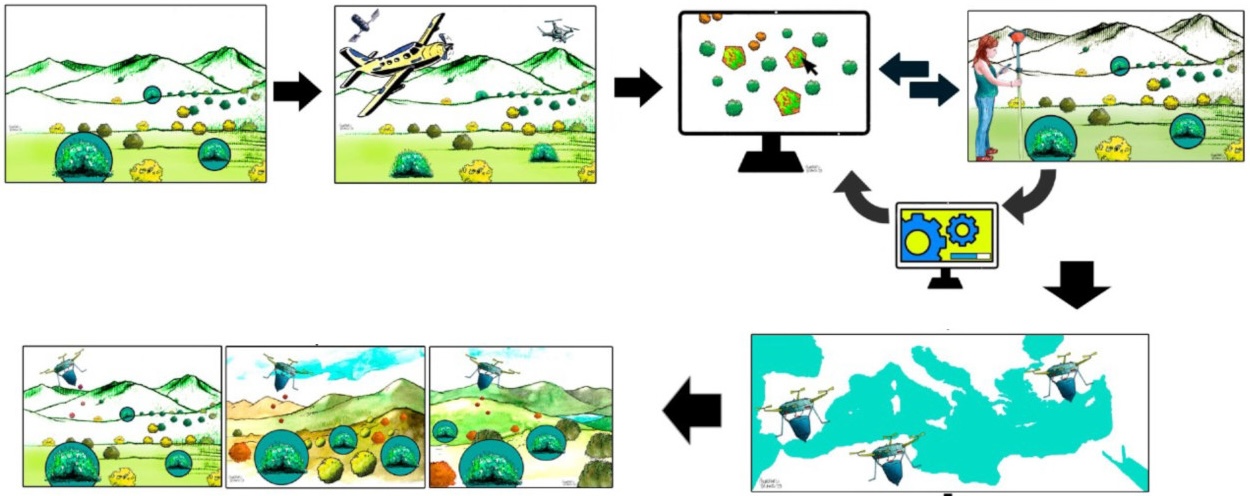
Drone seeding has great potential for forest restoration, but it is currently done inefficiently, scattering seeds across the entire area without distinguishing where they can actually grow. This leads to significant seed waste and low success rates. This article proposes a more precise approach: identifying small "microsites" suitable for planting using ecological knowledge, high-resolution imagery, and artificial intelligence, and then guiding the drone directly to those points. This strategy would require fewer seeds, reduce costs, and increase the likelihood of seedling survival and growth into trees.
See whole open source article on: Restoration Ecology
Exploring evolution and trends:
A bibliometric analysis and scientific mapping of multiobjective optimization applied to hybrid microgrid systems
June 17th, 2024
Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems integrate renewable sources, storage, and optionally conventional energies, offering an eco-friendly solution to fossil fuels. Microgrids bolster HRES integration, enhancing energy management, resilience, and reliability at various levels. This study, emphasizing the need for refined optimization methods, investigates three topics: renewable energy, microgrid, and multiobjective optimization, through a bibliometric analysis of 470 Scopus documents from 2010-2023, analyzed with an specific software.
See whole open source article on Sustainability

ROSETTA project:
Modelling and optimisation of micro-grids oriented to areas in the context of social crisis with impact on energy infrastructure; a new mathematical tools for self-generated time transformation.
The objective of the project is to study the viability and optimal typology of micro-grids including solar photovoltaic for supply energy as an alternative (or complement) to the use of the national energy grid in countries with dammaged electrical infrastructure, for example as a result of an armed conflict, and where load data is lacking.
Our approach is based on first understanding the geographical and energy realities of each area to establish patterns that allow consumption data to be generated immediately and with the use of very few parameters, generating a very useful tool for our study or any subsequent study.
Interdisciplinary research project C-ING-288-UGR23 of the Plan Propio UGR 2023, funded by Programa operativo FEDER Andalucía 2021-2027 de la JJAA.

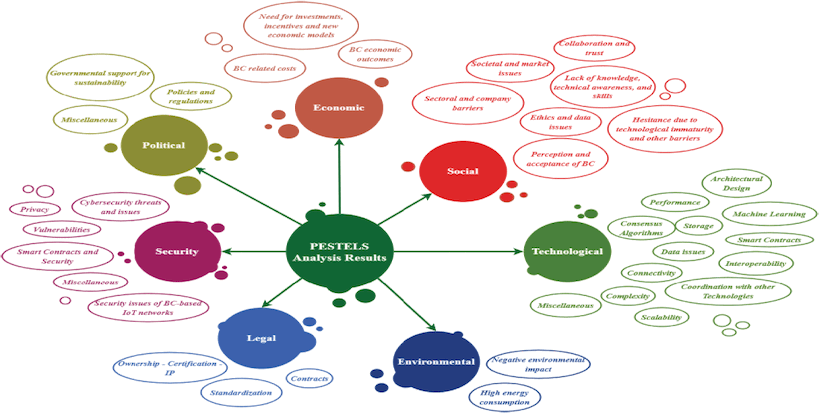
Blockchain is a disruptive technology ensuring the immutability of digital transactions. Initially used in cryptocurrencies, it now spans various sectors, including agriculture, which benefits from digitalization and Industry 4.0 technologies like IoT and Cyber-Physical Systems. Big Data shows promise in product traceability and agricultural supply chain management.
A review of 152 studies highlights current challenges and research opportunities, analyzed through the PESTELS framework (Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal, and Security), with significant technological hurdles driving potential advancements.
See whole open source article on IEEE Access
Forest restoration: more than firing seeds from a drone
January 2023
Although drone seeding is presented as a promising solution for reforesting large areas, there is still no clear scientific evidence of its success. Dropping seeds from the air does not guarantee they will grow, as they must overcome many natural obstacles. The article points out that, for this technology to work, it is key to increase precision: sowing only in the best locations, using fewer seeds, and reducing costs, instead of making massive, uncontrolled drops.
See whole open source article on Restoration Ecology

Although millions of trees are planted worldwide today, many initiatives overlook a fundamental aspect: ensuring that these trees survive and thrive. This article proposes "precision forest restoration", an approach that uses science and technology to care for each individual tree, creating stronger and more functional forests. While it requires a larger initial investment, it is more effective and sustainable in the long run.
See whole open source article on: Restoration Ecology

SUSTAINABLE project:
Stop running, stop and start using our knowledge to be reachable.
This project aims to develop and validate innovative Artificial Intelligence as Decision Support System for suitable precision agriculture management procedures according to the specific climate, geographical, and environmental conditions. This will give optimized solutions in terms of energy efficiency, water consumption, and reuse, also in extreme conditions as we increasingly witness due to climate changes.
Research project Ref. 101007702, funded by the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie RISE Grant Agreement


















